By: Bode Thomas Adeyemi, PhD
Introduction
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) is a global development strategy launched by the Chinese government in 2013 under President Xi Jinping. The initiative aims to enhance international trade and economic integration by building infrastructure and fostering investments across Europe, Asia, Africa, and beyond. The BRI is often described as a modern-day Silk Road, reflecting its goals to revitalize ancient trade routes and promote connectivity.
Key Components of the BRI
1. Infrastructure Development: The BRI focuses on developing physical infrastructure, such as roads, railways, ports, and airports, to improve trade connectivity between participating countries.
2. Economic Corridors: The initiative includes the establishment of various economic corridors, such as the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) and the China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor, aiming to facilitate trade and enhance regional economic cooperation.
3. Investment and Financing: The BRI involves significant Chinese investments in participating countries, often financed by Chinese banks and institutions, to support infrastructure and economic development projects.
4. Cultural Exchange and Cooperation: Besides infrastructure and economic ties, the BRI emphasizes cultural exchange, education, and people-to-people connections between participating countries to foster mutual understanding and collaboration.
5. Sustainability and Green Development: Recently, there has been an increasing focus on promoting sustainable development practices within the BRI framework, including investments in renewable energy and environmentally friendly projects.
Goals of the BRI
- Enhancing Global Trade: The BRI aims to facilitate smoother and more efficient trade routes by improving connectivity and logistics.
- Economic Development: The initiative promotes economic growth in developing countries by investing in essential infrastructure.
- Strengthening Political and Economic Ties: The BRI aims to forge stronger diplomatic relationships between China and participating nations, enhancing cooperation in various sectors.
Lessons Learned for Project Managers
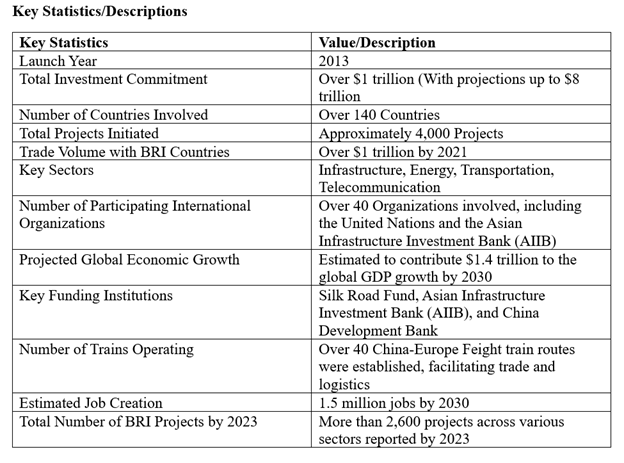
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), launched by China in 2013, represents one of modern history's largest and most ambitious global development projects. The BRI aims to enhance global connectivity and foster economic collaboration by encompassing infrastructure, trade routes, and investment across over 140 countries. For project managers, the BRI offers numerous critical lessons applicable to large-scale international projects and any complex initiative requiring extensive coordination, cooperation, and strategic planning. Below are several key lessons learned for project managers from the BRI experience:
1. Strategic Planning and Flexibility
One of the most significant lessons for project managers is the necessity of thorough strategic planning and the flexibility to adapt to changing circumstances. The BRI spans diverse geographic regions with varying political, economic, and cultural contexts. Project managers must be equipped to navigate unforeseen challenges, such as political instability, economic fluctuations, or local regulations. Developing a robust yet flexible project plan can enable teams to respond effectively to dynamic environments.
2. Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
The diverse range of stakeholders involved in the BRI highlights the importance of effective communication and engagement. Project managers should prioritize establishing open communication channels with all stakeholders—governments, local communities, investors, and contractors. Understanding stakeholder interests, concerns, and expectations can build trust and facilitate smoother project execution. Regular updates and consultations can help mitigate conflicts and align the parties' objectives.
3. Risk Management
The BRI has encountered various risks, including geopolitical tensions, financial uncertainties, and environmental concerns. Project managers can learn the importance of comprehensive risk assessment and management strategies. Identifying potential risks early on, developing detailed contingency plans, and continuously monitoring project environments can help minimize adverse impacts. Diversification of funding sources and partnerships can also mitigate financial risks associated with large-scale investments.
4. Cultural Sensitivity and Local Expertise
Operating in diverse regions necessitates a deep understanding of local customs, cultures, and business practices. BRI projects have experienced both successes and challenges based on the level of cultural sensitivity and local engagement. Project managers should prioritize hiring local experts and building teams that reflect the cultural contexts of the project’s location. This approach enhances communication and cooperation and fosters community support, increasing the likelihood of project success.
5. Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
The BRI offers critical lessons about integrating sustainability into project planning as global scrutiny grows regarding environmental impacts. Project managers should adopt practices that prioritize environmental protection and sustainable resource management. Engaging with environmental stakeholders and conducting thorough environmental assessments can help projects align with both global standards and local expectations, ensuring long-term viability.
6. Capacity Building and Knowledge Transfer
The BRI has emphasized the need for capacity building in partner nations. Project managers should focus on executing projects and empowering local communities through knowledge transfer and skills development. Training programs, workshops, and collaborative opportunities can enhance local expertise, fostering sustained economic development beyond the project's life cycle.
7. Monitoring and Evaluation
An essential aspect of successful project management is the implementation of effective monitoring and evaluation (M&E) frameworks. The BRI’s complex nature necessitates ongoing assessment to gauge progress, efficiency, and impact. Project managers should establish clear metrics for evaluating project outcomes and regularly review them to ensure alignment with original goals. Learning from both successes and setbacks enables continuous improvement and enhances future project planning.
8. Public-Private Partnerships (PPP)
The BRI illustrates the importance of engaging in effective public-private partnerships to leverage resources, expertise, and risk sharing. Project managers should recognize the advantages of PPP models that can facilitate funding and resource mobilization and drive innovation. Building strong partnerships between government bodies and private sector players can enhance project execution and sustainability.
9. Long-term Vision and Commitment
Successful projects require a long-term perspective and commitment beyond the initial implementation phases. The BRI emphasizes that infrastructure and development projects often span multiple years or even decades. Project managers should set realistic timelines and be prepared for long-term engagement, ensuring that all stakeholders remain committed to the project’s goals throughout its lifecycle.
10. Inter-Agency Coordination
Effective inter-agency coordination is crucial given the scale and multitude of stakeholders involved in BRI projects. Project managers can learn from the necessity of synchronizing efforts among various governmental departments, NGOs, and international bodies to achieve cohesive and efficient project delivery. This may involve establishing coordination committees or task forces to streamline efforts.
Conclusion
China’s Belt and Road Initiative is not just an ambitious plan for global infrastructure development; it serves as a potent case study from which project managers can glean critical lessons for managing complex, large-scale projects. Emphasizing strategic planning, stakeholder engagement, risk management, cultural sensitivity, sustainability, capacity building, continuous monitoring, and effective partnerships can significantly improve project management. The BRI illustrates that successful project management requires a holistic approach, acknowledging the interconnectedness of global challenges and fostering collaborative solutions to achieve shared objectives.
The initiative emphasizes the need for adaptability, collaboration, and long-term commitment to ensure sustainability and generate lasting benefits for local communities. As globalization continues to shape the landscape of project management, the insights gained from the BRI can guide professionals in fostering resilient partnerships, leveraging local expertise, and implementing innovative solutions. Ultimately, these lessons equip project managers to achieve project goals and contribute meaningfully to global development objectives. By embracing these principles, they can navigate challenges effectively and pave the way for future international cooperation and success.
